 Nozomi Takai, Yukari Tanaka, Kazuhiro Inazawa and Hideo Saji
Nozomi Takai, Yukari Tanaka, Kazuhiro Inazawa and Hideo Saji
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. (2012), 26(13), 1549-1556
RATIONALE: Recently, the requirement for a quantitative research method using imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) to be developed has been discussed. Specifically, the simultaneous quantification of a drug in multiple organs by using whole-body sections could be insightful for the pharmaceutical industry in the study of drug distribution.
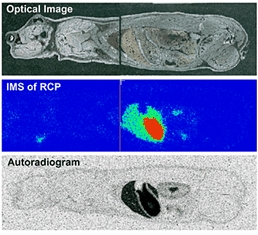
METHODS: Frozen whole-body sections were obtained from mice injected with raclopride, a dopamine D2 receptor selective antagonist, and coated with a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) matrix compound. The whole-body sections were then analyzed using a linear ion trap mass spectrometer equipped with a MALDI source. The concentration of raclopride in each tissue was determined using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS).
RESULTS: The IMS-based signal intensity of raclopride strongly correlated with the concentration of the drug in the tissue samples (R = 0.94; p <0.001) of six different organs. Furthermore, the spatial information obtained by IMS was very similar to that obtained by autoradiography, which is a traditional technique used for the study of drug distribution.
CONCLUSIONS: This study suggests that IMS enables the quantitative analysis of drug distribution in multiple organs simultaneously. In addition, it enhances ideal drug candidate selection in terms of efficient evaluations.
No responses yet